| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28286-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Language Reference 11g Release 1 (11.1) Part Number B28286-01 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the ALTER OPERATOR statement to add bindings to, drop bindings from, or compile an existing operator.
See Also:
CREATE OPERATORPrerequisites
The operator must already have been created by a previous CREATE OPERATOR statement. The operator must be in your own schema or you must have the ALTER ANY OPERATOR system privilege. You must have the EXECUTE object privilege on the operators and functions referenced in the ALTER OPERATOR statement.
Syntax
alter_operator::=
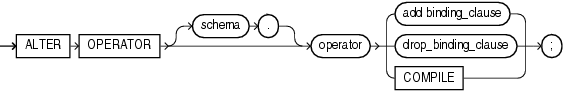
(add_binding_clause::=, drop_binding_clause::=)
(implementation_clause::=, using_function_clause::=)
Semantics
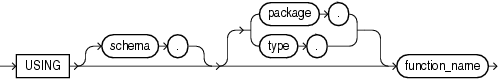
schema
Specify the schema containing the operator. If you omit this clause, then Oracle Database assumes the operator is in your own schema.
operator
Specify the name of the operator to be altered.
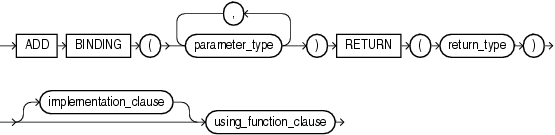
Use this clause to add an operator binding and specify its parameter datatypes and return type. The signature must be different from the signature of any existing binding for this operator.
If a binding of an operator is associated with an indextype and you add another binding to the operator, then Oracle Database does not automatically associate the new binding with the indextype. If you want to make such an association, then you must issue an explicit ALTER INDEXTYPE ... ADD OPERATOR statement.
implementation_clause
This clause has the same semantics in CREATE OPERATOR and ALTER OPERATOR statements. For full information, refer to implementation_clause in the documentation on CREATE OPERATOR.
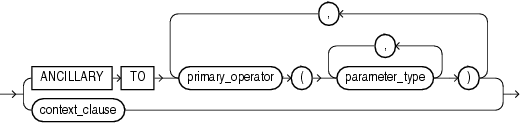
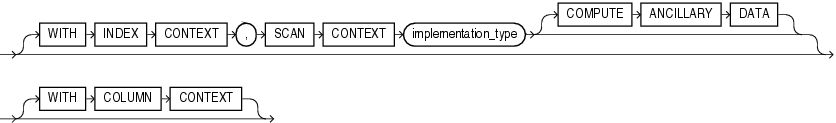
context_clause
This clause has the same semantics in CREATE OPERATOR and ALTER OPERATOR statements. For full information, refer to context_clause in the documentation on CREATE OPERATOR.
using_function_clause
This clause has the same semantics in CREATE OPERATOR and ALTER OPERATOR statements. For full information, refer to using_function_clause in the documentation on CREATE OPERATOR.
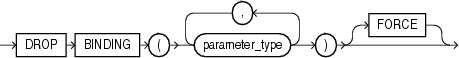
Use this clause to specify the list of parameter datatypes of the binding you want to drop from the operator. You must specify FORCE if the binding has any dependent objects, such as an indextype or an ancillary operator binding. If you specify FORCE, then Oracle Database marks INVALID all objects that are dependent on the binding. The dependent objects are revalidated the next time they are referenced in a DDL or DML statement or a query.
You cannot use this clause to drop the only binding associated with this operator. Instead you must use the DROP OPERATOR statement. Refer to DROP OPERATOR for more information.
COMPILE
Specify COMPILE to cause Oracle Database to recompile the operator.
Examples
Compiling a User-defined Operator: Example The following example compiles the operator eq_op (which was created in "Creating User-Defined Operators: Example"):
ALTER OPERATOR eq_op COMPILE;